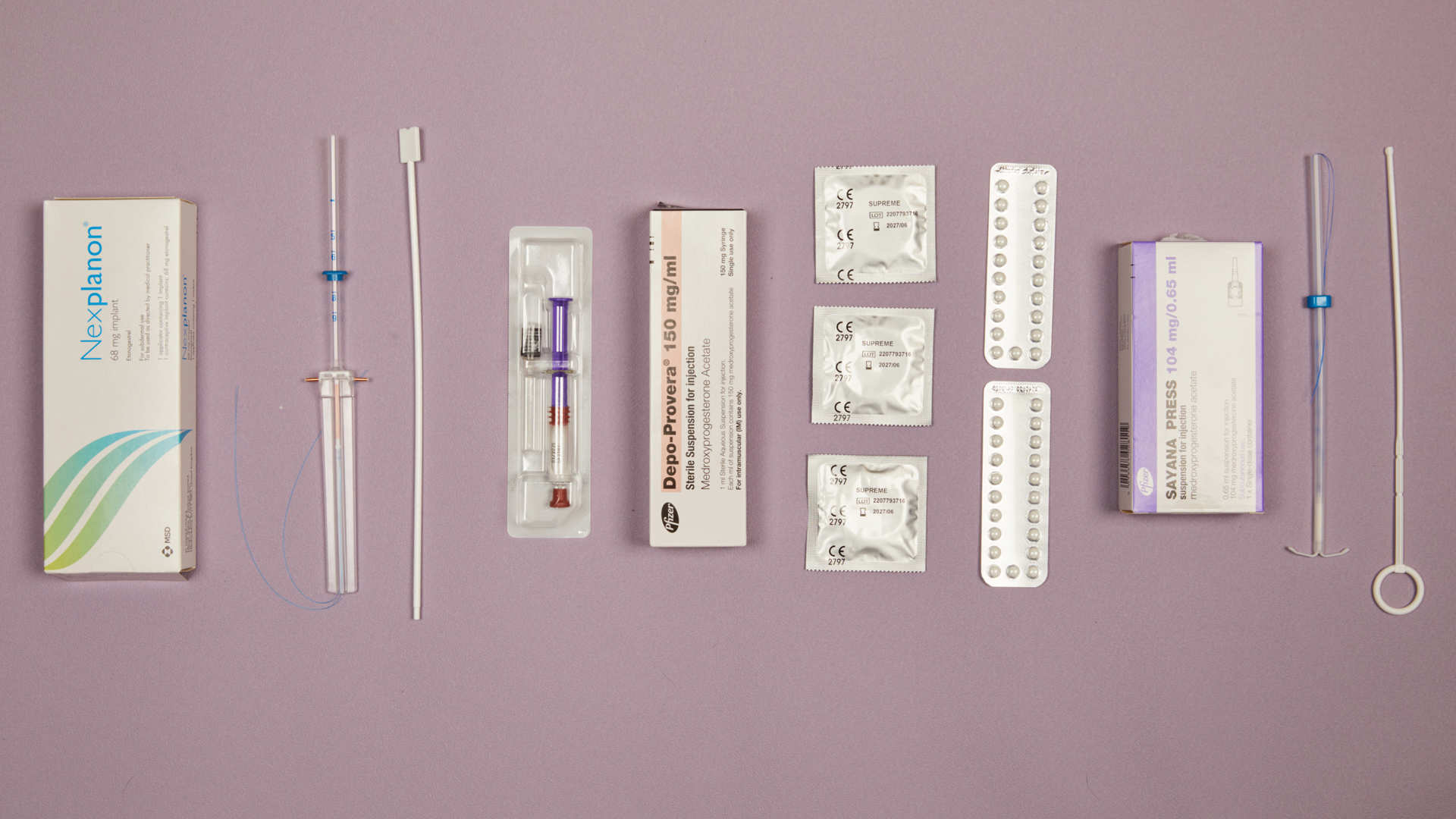
We can arrange to have your method of contraception ready straight after your treatment.
You may have already discussed this with one of our contraception nurses over the telephone. If not, we will talk with you about your preferred contraception during your medical assessment.
We can usually supply your initial contraception while you are with us, so you won’t have to arrange an immediate appointment with your GP or local family planning service. However, you may need to contact these services for your future contraceptive needs.
Contraception: Frequently asked questions
You might have lots of questions which we are happy to answer when you call or visit the clinic. We answer some of the things people ask and give links for more information below:
-
Can I get pregnant at any time of my cycle?
-
Yes, although the chances of getting pregnant at the beginning or end of your cycle are very low. The problem is, if you don't want to be pregnant, you can't take chances.
While it will vary from woman to woman, you are usually most fertile around 2 weeks before your next period is due. This is when an egg is released from your ovaries (ovulation).
Sperm can live for up to 5 days inside you, so even if you have sex early on in your cycle there is a possibility sperm will still be there when you ovulate and the egg will be fertilised. If you ovulate early, it would be possible to get pregnant shortly after your period finishes.
Some women think if they've had unprotected sex a few times and not become pregnant that they may be infertile, but all this suggests is they probably weren't having sex at their fertile time.
If you've had unprotected sex and don't want to be pregnant, use emergency contraception as soon as possible after it's happened.
-
Does abortion lead to infertility?
-
No, although it is something that those opposed to abortion may say. There is absolutely no evidence that safe, legal abortion will lead to infertility. In fact, after an abortion, fertility returns almost immediately.
-
I've just stopped using hormonal contraception - will it take a while for fertility to return?
-
There is a myth that it takes some time for the hormones to leave your body before your fertility kicks in again.
The truth is you can get pregnant very soon after you stop using most hormonal contraception (which is why women can conceive when they miss pills or have had a tummy bug), so you need to use another method of contraception if you want to avoid pregnancy. The same is also true of a copper IUD (the coil) - once removed, your fertility quickly returns to normal.
With the Depo-Provera injection, it can take up to a year for fertility to return once you stop the injection, but there is no guarantee. So again, if you want to avoid pregnancy, you need to use contraception straight away.
-
I'm worried the emergency contraceptive pill may have harmed my fertility- is this likely?
-
There is no evidence to show that taking the emergency contraceptive pill, even repeatedly, will affect your future fertility. The most widely used emergency contraceptive pill is Levonelle®. It's very safe and contains less than half the active hormone contained in a monthly cycle of normal contraceptive pills. It can be used more than once in one cycle if needed. The hormone leaves your body within days, so you need to use another form of contraception to protect against pregnancy if you have sex again during that cycle.
The other emergency contraceptive pill is EllaOne®, which appears to be more effective than Levonelle® in women who weigh around 12 stone or more (75kg), and provides very high protection against unwanted pregnancy for up to 5 days after unprotected sex. It should not be used more than once per cycle, and if you've taken it because you missed your regular contraceptive pill you need to use condoms as well as your usual pills for the next 14 days.
-
I've recently had a baby - do I need to use contraception?
-
If it's been 3 weeks or more since the birth of your baby, you need to use contraception if you don't want to get pregnant again straightaway. Exclusively breastfeeding can be an extremely effective method of contraception but you need to be feeding very regularly (at least every 4 hours during the day and every 6 hours at night), your baby must be less than 6 months old, and your periods must not have returned. Soothers and expressing milk also make it less effective.
There are many safe methods of contraception you can use while breastfeeding that won't harm your baby or milk supply, so talk to your doctor or midwife to help you find one that's right for you ... more
